SHARE
Liquid Metal Batteries- Is this the next Green Revolution?
Liquid Metal Batteries are a novel large-scale electricity storage technology and it seems that Cambridge based MIT recently reached a breakthrough to make these batteries longer-lasting and cheaper, which could lead to an Energy revolution and the future of batteries.
The new, improved technology could help to make renewable energy such as wind and solar help compete against conventional power plants. The current problem sounds simple but is rather hard to solve. The sun only shines during the daytime and the blowing of wind is also not stable and predictable so that there will always be peaks and lows in energy production from these sources. To integrate them properly into the grid and to make them profitable, the energy has to be stored and released, when it is needed. And unlike for potatoes, gasoline and huge amounts of data, the technology for electricity storage is still very basic.
The system that is currently used to store electricity, is pumped-hydro, in which water is pumped uphill, where it is stored until it is needed and then it runs downhill, through a turbine with a generator. The limits to this solution, are again very down-to-earth and still hard to solve. You need a mountain and a lot of water. The round-trip-efficiency of such a solution is around 70%. Check here for more info on pumped hydro.
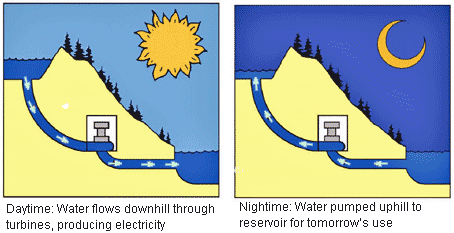 Source foto Pumped hydro www.water.usgs.gov
The newest generation of Liquid Metal Batteries is able to achieve the same efficiency, but the technology is still in its early stage and scientists expect rapid evolvement. Sadoway, the John F. Elliott Professor of Materials Chemistry, and father of the Liquid Metal Battery says that because there has been little commercial interest in exploring the properties and potential uses of liquid metals and alloys of the type that are most attractive as electrodes for liquid metal batteries, “I think there’s still room for major discoveries in this field.” more
Robert Metcalfe, professor of innovation at the University of Texas at Austin, who was not involved in this work, says, “The Internet gave us cheap and clean connectivity using many kinds of digital storage. Similarly, we will solve cheap and clean energy with many kinds of storage. Energy storage will absorb the increasing randomness of energy supply and demand, shaving peaks, increasing availability, improving efficiency, lowering costs.”more
Technology insight:
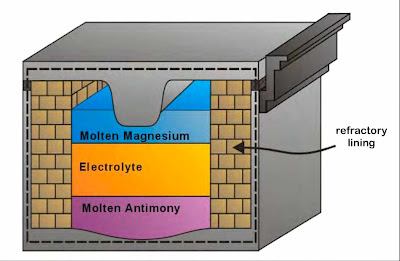
The cells are made of three simple components: a salt (electrolyte)
which separates two distinct liquid metal layers (electrodes). Cells operate at elevated
temperatures 450-500°C and, upon melting, the three layers self-segregate and float on top of one
another due to their different densities and levels of immiscibility. In a charged state, there
is potential energy between the top metal layer and the bottom metal layer which creates
a cell voltage.
Source foto Pumped hydro www.water.usgs.gov
The newest generation of Liquid Metal Batteries is able to achieve the same efficiency, but the technology is still in its early stage and scientists expect rapid evolvement. Sadoway, the John F. Elliott Professor of Materials Chemistry, and father of the Liquid Metal Battery says that because there has been little commercial interest in exploring the properties and potential uses of liquid metals and alloys of the type that are most attractive as electrodes for liquid metal batteries, “I think there’s still room for major discoveries in this field.” more
Robert Metcalfe, professor of innovation at the University of Texas at Austin, who was not involved in this work, says, “The Internet gave us cheap and clean connectivity using many kinds of digital storage. Similarly, we will solve cheap and clean energy with many kinds of storage. Energy storage will absorb the increasing randomness of energy supply and demand, shaving peaks, increasing availability, improving efficiency, lowering costs.”more
Technology insight:
The cells are made of three simple components: a salt (electrolyte)
which separates two distinct liquid metal layers (electrodes). Cells operate at elevated
temperatures 450-500°C and, upon melting, the three layers self-segregate and float on top of one
another due to their different densities and levels of immiscibility. In a charged state, there
is potential energy between the top metal layer and the bottom metal layer which creates
a cell voltage.
 Source Foto www.investorintel.com
The research has been funded to the tune of $15m by the likes of Bill Gates, energy giant Total, the US Department of Energy’s Advanced Research Projects Agency, and Khosla Ventures. more
With these strong supporters in the back, this new Technology has the potential to fundamentally change the way power grids are operated on a global basis.
Our next blog will discuss another hot topic and another potential revolution for the Energy Industry. Are you involved in any of these Technologies?
Check out our Energy efficiency challenges!
Source Foto www.investorintel.com
The research has been funded to the tune of $15m by the likes of Bill Gates, energy giant Total, the US Department of Energy’s Advanced Research Projects Agency, and Khosla Ventures. more
With these strong supporters in the back, this new Technology has the potential to fundamentally change the way power grids are operated on a global basis.
Our next blog will discuss another hot topic and another potential revolution for the Energy Industry. Are you involved in any of these Technologies?
Check out our Energy efficiency challenges!
 Source foto Pumped hydro www.water.usgs.gov
The newest generation of Liquid Metal Batteries is able to achieve the same efficiency, but the technology is still in its early stage and scientists expect rapid evolvement. Sadoway, the John F. Elliott Professor of Materials Chemistry, and father of the Liquid Metal Battery says that because there has been little commercial interest in exploring the properties and potential uses of liquid metals and alloys of the type that are most attractive as electrodes for liquid metal batteries, “I think there’s still room for major discoveries in this field.” more
Robert Metcalfe, professor of innovation at the University of Texas at Austin, who was not involved in this work, says, “The Internet gave us cheap and clean connectivity using many kinds of digital storage. Similarly, we will solve cheap and clean energy with many kinds of storage. Energy storage will absorb the increasing randomness of energy supply and demand, shaving peaks, increasing availability, improving efficiency, lowering costs.”more
Technology insight:
The cells are made of three simple components: a salt (electrolyte)
which separates two distinct liquid metal layers (electrodes). Cells operate at elevated
temperatures 450-500°C and, upon melting, the three layers self-segregate and float on top of one
another due to their different densities and levels of immiscibility. In a charged state, there
is potential energy between the top metal layer and the bottom metal layer which creates
a cell voltage.
Source foto Pumped hydro www.water.usgs.gov
The newest generation of Liquid Metal Batteries is able to achieve the same efficiency, but the technology is still in its early stage and scientists expect rapid evolvement. Sadoway, the John F. Elliott Professor of Materials Chemistry, and father of the Liquid Metal Battery says that because there has been little commercial interest in exploring the properties and potential uses of liquid metals and alloys of the type that are most attractive as electrodes for liquid metal batteries, “I think there’s still room for major discoveries in this field.” more
Robert Metcalfe, professor of innovation at the University of Texas at Austin, who was not involved in this work, says, “The Internet gave us cheap and clean connectivity using many kinds of digital storage. Similarly, we will solve cheap and clean energy with many kinds of storage. Energy storage will absorb the increasing randomness of energy supply and demand, shaving peaks, increasing availability, improving efficiency, lowering costs.”more
Technology insight:
The cells are made of three simple components: a salt (electrolyte)
which separates two distinct liquid metal layers (electrodes). Cells operate at elevated
temperatures 450-500°C and, upon melting, the three layers self-segregate and float on top of one
another due to their different densities and levels of immiscibility. In a charged state, there
is potential energy between the top metal layer and the bottom metal layer which creates
a cell voltage.
 Source Foto www.investorintel.com
The research has been funded to the tune of $15m by the likes of Bill Gates, energy giant Total, the US Department of Energy’s Advanced Research Projects Agency, and Khosla Ventures. more
With these strong supporters in the back, this new Technology has the potential to fundamentally change the way power grids are operated on a global basis.
Our next blog will discuss another hot topic and another potential revolution for the Energy Industry. Are you involved in any of these Technologies?
Check out our Energy efficiency challenges!
Source Foto www.investorintel.com
The research has been funded to the tune of $15m by the likes of Bill Gates, energy giant Total, the US Department of Energy’s Advanced Research Projects Agency, and Khosla Ventures. more
With these strong supporters in the back, this new Technology has the potential to fundamentally change the way power grids are operated on a global basis.
Our next blog will discuss another hot topic and another potential revolution for the Energy Industry. Are you involved in any of these Technologies?
Check out our Energy efficiency challenges!